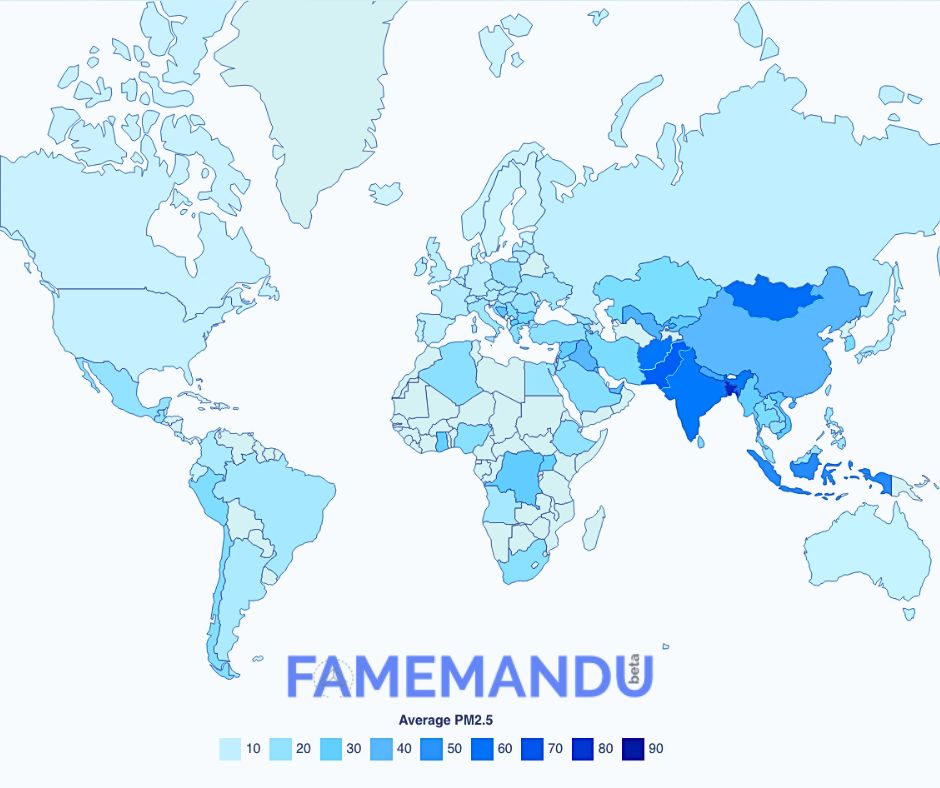
1. Bangladesh
Bangladesh faces serious environmental problems, mostly related to air and water pollution. High levels of air pollution are caused by rapid industry and urbanization, putting the quality of the air in crowded cities like Dhaka at danger. The issue is made worse by industrial discharges, vehicle pollution, and poor waste management. Water bodies, such as rivers like the Buriganga, are contaminated by untreated sewage and industrial effluents. Pollution has detrimental effects on biodiversity, public health, and the general state of the environment. Initiatives to promote sustainable practices, environmental awareness campaigns, and regulatory measures are some of the ways that these concerns are being addressed. Persistent pollution presents serious obstacles to Bangladesh’s environmental sustainability and people welfare, although continuous efforts.

2. Pakistan
Pakistan has a wide range of complicated pollution problems, including soil, water, and air pollution. Urban regions, particularly Karachi and Lahore, suffer greatly from air pollution caused by burning biomass, industrial activity, and vehicle emissions. Air quality issues are made worse by enterprises using antiquated technologies. Rivers such as the Indus are affected by significant water pollution caused by untreated sewage, agricultural runoff, and industrial effluents. Dirty soil is a result of inappropriate solid waste disposal. These pollution issues have a significant impact on public health because they can cause waterborne and respiratory ailments. To counteract the damaging impacts of pollution on the environment and the populace, Pakistan is striving to enact environmental laws, improve waste management techniques, and encourage sustainable growth.

3. Mongolia
Significant pollution problems exist in Mongolia, especially in Ulaanbaatar, the country’s capital. Traditional stove use is a major source of air pollution with high particulate matter (PM) levels, especially during the cold winter months. When coal and other solid fuels are burned for heating, harmful particles are released into the air that can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular problems. Apart from the pollutants produced by households, air pollution is also caused by industrial operations and the mining industry. The ecosystem and general public’s health are negatively impacted by the excessive dust and particle matter levels. A number of measures have been put forth to address this problem, such as campaigns to raise awareness of sustainable behaviors, initiatives to minimize coal consumption, and the promotion of cleaner technologies. In spite of continuous efforts, air pollution in Mongolia continues to be a major concern.

4. Afghanistan
Afghanistan suffers from a variety of environmental issues, such as contaminated air and water, which are made worse by years of violence and poor infrastructure. The main causes of the severe air pollution in the capital city of Kabul include dust, solid fuel combustion, and emissions from moving vehicles. Ecology problems are made worse by improper waste management. Rivers tainted by agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and insufficient sewage treatment are common sources of water pollution. These pollution issues have a negative impact on respiratory systems and waterborne illnesses, among other negative health implications. The delicate ecosystem of the nation is further strained by environmental degradation. Afghanistan’s pollution problem calls for comprehensive solutions, such as upgraded waste management systems, sustainable practices, and better infrastructure, in order to protect the environment and public health in the face of persistent sociopolitical difficulties.

5. India
India faces numerous challenges related to pollution, especially in the air and water. Severe air pollution is mostly caused by agricultural practices, vehicle emissions, and rapid development, especially in large cities like Delhi. The issue is made worse by burning solid fuels and agricultural waste. Industrial discharges, insufficient sewage treatment, and agricultural runoff all contribute to widespread water pollution. Contamination of rivers, such as the Ganges, affects aquatic ecosystems and public health. Additives and inappropriate waste management are frequently associated with soil pollution, which presents more environmental difficulties. Pollution’s cumulative impacts lead to respiratory disorders, waterborne infections, and ecological destruction. India is addressing these problems and promoting sustainable habits by developing legislative measures, greener technologies, and public awareness initiatives.